How to Install and Configure a GitLab Runner on Ubuntu 18.04
Introduction
This guide provides detailed steps to install, register, and configure a GitLab Runner on Ubuntu 18.04. By following these instructions, you will set up a GitLab Runner to automate your CI/CD processes.
Install GitLab Runner manually on GNU/Linux
Adding the GitLab Official Repository
First, download the GitLab Runner executable appropriate for your system architecture
# Linux x86-64
$ sudo wget -O /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/binaries/gitlab-runner-linux-amd64
# Linux x86
$ sudo wget -O /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/binaries/gitlab-runner-linux-386
# Linux arm
$ sudo wget -O /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/binaries/gitlab-runner-linux-arm
Give it permission to execute
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runnerCreate a dedicated user for running GitLab CI processes
$ sudo useradd --comment 'GitLab Runner' --create-home gitlab-runner --shell /bin/bashInstall and start the GitLab Runner as a service
$ sudo gitlab-runner install --working-directory /home/project/gitlab-runner-builds --user <vps-user>
$ sudo gitlab-runner startImportant Note
When the GitLab Runner is installed and running as a service, it operates under the root user but executes jobs as the user specified during the install. This user must have sufficient permissions to access the gitlab-runner executable for job functions like handling caches and artifacts.
Next step is to register the runner.
Registering the GitLab Runner
To register a Runner under GNU/Linux:
1. Run the following command:
$ sudo gitlab-runner register2. Enter your GitLab instance URL:
Please enter the gitlab-ci coordinator URL (e.g. https://gitlab.com )
$ https://gitlab.com3. Enter the token you obtained to register the Runner:
Please enter the gitlab-ci token for this runner
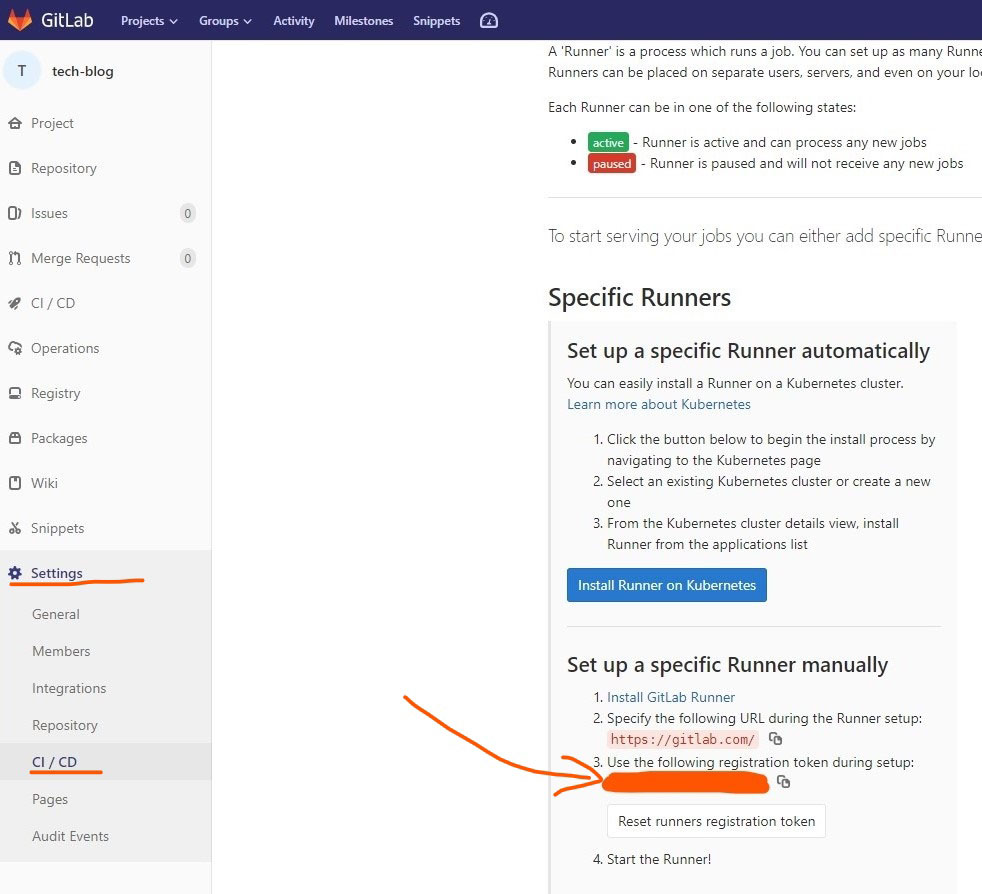
$ <your-token-id>Your gitlab-ci token id can be copied from your account
Your-Project-repository→ Settings → CI/CD → Runners → Specific Runners → token-id ( see the image below )
4. Enter a description for the Runner, you can change this later in GitLab’s UI:
Please enter the gitlab-ci description for this runner
$ [hostame] my-runner5. Enter the Runner executor:
In this case we chose shell
Please enter the executor: ssh, docker+machine, docker-ssh+machine, kubernetes, docker, parallels, virtualbox, docker-ssh, shell:
$ shellConclusion
Following these steps will configure a GitLab Runner on your Ubuntu system, ready to automate your CI/CD workflows. Remember to regularly update the Runner and monitor its performance to maintain efficient operations.